By: Victoria Iyeduala (Freelance Health and Wellness Writer)
 Despite the risks associated with especially inappropriate self-medication, people still practise it frequently.
Despite the risks associated with especially inappropriate self-medication, people still practise it frequently.
People usually use it as a first line of treatment when they fall ill.
Research shows that some people continue to self-medicate for various mild to serious ailments despite being aware of the dangers or consequences associated with it.
The consequences of self-medication will be explained from two viewpoints:
Proposals on how to tackle harmful self-medication in order to reduce or totally eliminate its impact will be discussed in another report.
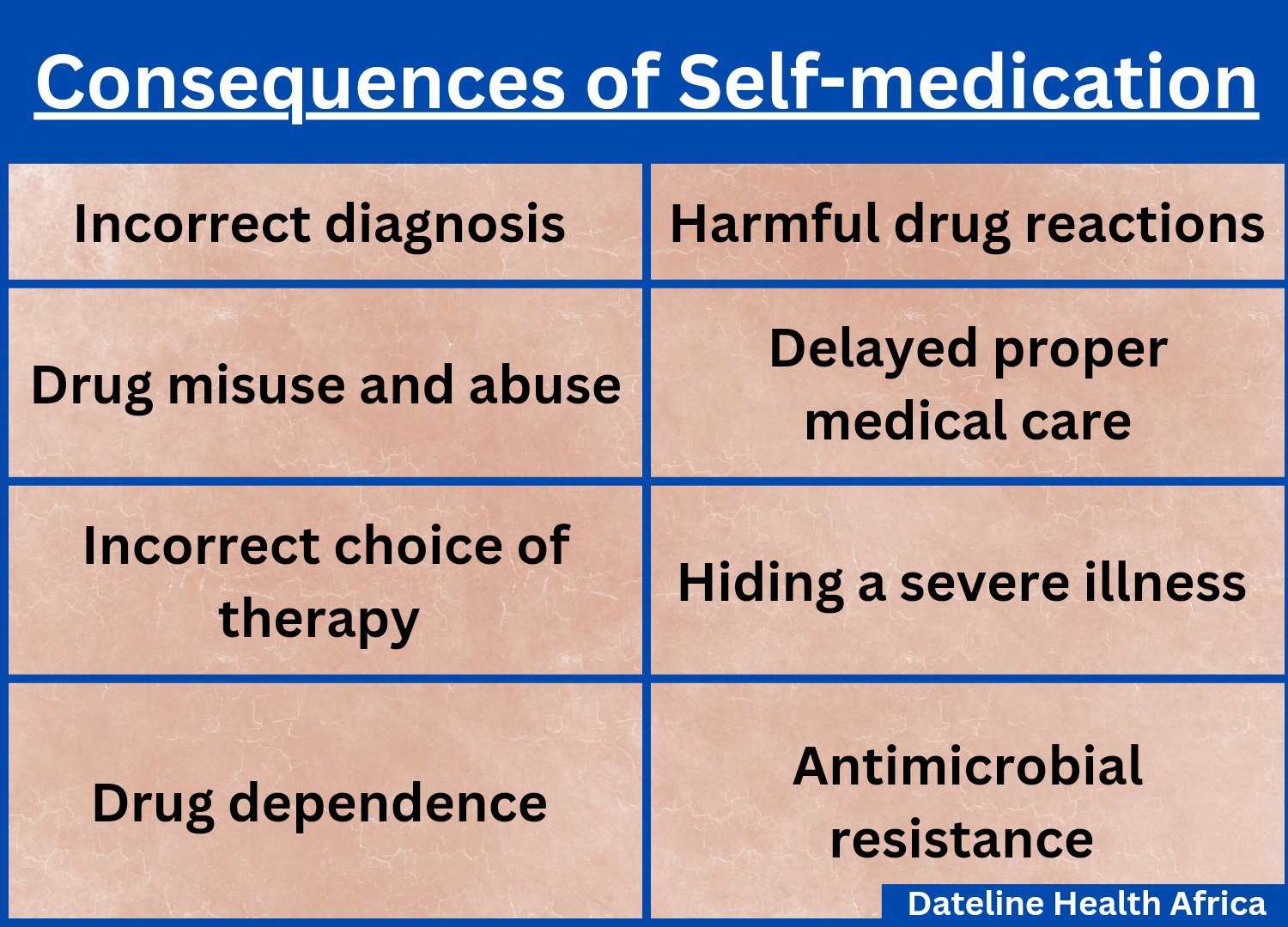 One of the most common risks of self-medication is incorrect diagnosis. During self-medication, you may misdiagnose yourself with an illness. This is because you don't have the right knowledge to diagnose yourself correctly.
One of the most common risks of self-medication is incorrect diagnosis. During self-medication, you may misdiagnose yourself with an illness. This is because you don't have the right knowledge to diagnose yourself correctly.
For example, you may treat yourself for malaria when you don't have malaria or when you have another high temperature (fever) inducing sickness. This is dangerous because you may find out later that you have a significant illness that requires immediate proper care.
Self-medication increases the risk of drug misuse – non-prescription (OTC), prescription and herbal medicine. You may take the wrong medicine or an incorrect dosage or administer the drug wrongly.
Because of the pleasant effects or feelings you get from regularly using a drug such as opioids and alcohol, you may start using these drugs for the sole reason of experiencing these feelings. This is drug abuse.
Some illnesses may not require taking drugs. In treating yourself without guidance from the right healthcare professional, you may be taking drugs for an illness requiring other forms of care like surgery or psychotherapy to recover quickly.
Using drug therapy or taking medication for this illness may prove ineffective. This means you could have this sickness for a long time because you're not receiving the right treatment.
For example, you could be taking drugs for a mental health illness requiring psychotherapy or talk therapy to get well. Or you may require a combination of the two for better recovery.
Some drugs do not go well together. When used together, these drugs can make you feel unwell or worsen your condition. Interaction between medications may also cause drug-induced illnesses.
Food-drug interactions can also occur. This is when the food you eat affects your medications or vice versa. These interactions can be harmful to your health.
Without adequate information or the right advice, you may use a medication containing allergic substances.
While practising self-medication, you may use drugs that are meant for a different group of people. For example, a child taking an adult's medication or a pregnant woman taking antibiotics that she's not supposed to take in her condition.
Complications from taking these drugs can be minor or life-threatening.
When you self-medicate, you put off getting the right medical counsel, diagnosis and care, especially if your symptoms improve. When an illness is diagnosed early, it can be treated properly on time to increase your chance of quick recovery.
You might take the wrong medications even though you know the sickness you're treating. Seeking expert medical advice and care will ensure that you're getting the right treatment for that illness to get well soon.
Practising self-medication increases your risk of being unaware of a severe illness. Since self-medication might delay proper diagnosis, you can be unaware that you have a serious or chronic health issue since you've been self-medicating for the wrong illness.
Some medications may conceal the symptoms of an underlying health condition. You could also be treating the symptoms caused by an underlying health condition you are unaware of.
Using drugs without a prescription can lead to repetitive and damaging use over a long period.
When you self-medicate on recreational drugs or substances, you may end up uncontrollably craving the pleasant effects of these drugs. This may make you use them continuously and unnecessarily to function or not function well and you may fall ill when you stop using.
Substance use disorder or drug addiction negatively interferes with all aspects of one's life, including education, work, marriage and health.
If you or someone you know is self-medicating on recreational drugs or substances, seek professional help early in order to stop its harmful health and mental effects.
According to the WHO, "Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites change over time and no longer respond to medicines making infections harder to treat and increasing the risk of disease spread, severe illness and death."
When the available drugs no longer work on these disease-causing agents, sicknesses become harder to treat and cure.
You risk developing AMR or drug resistance if you frequently misuse or overuse antimicrobial drugs such as antibiotics and antimalarials through inappropriate self-medication.
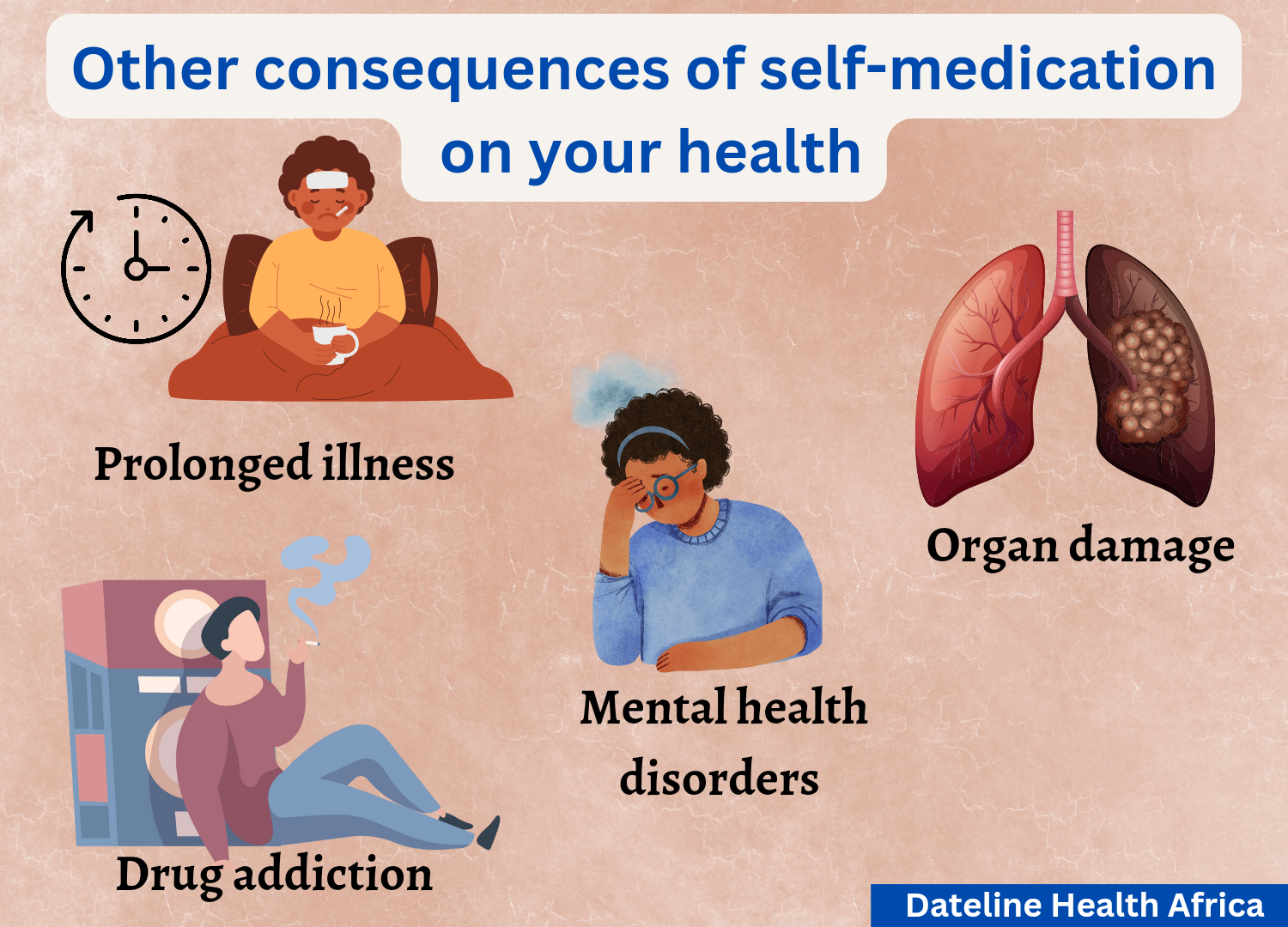 A person may suffer from an illness for a long time due to self-medication or end up treating an illness for a long time before it goes away.
A person may suffer from an illness for a long time due to self-medication or end up treating an illness for a long time before it goes away.
Incorrect self-diagnosis or misdiagnosis, delay in seeking professional medical care and antimicrobial resistance can prolong treatment for an illness or slow recovery.
Drug interactions interfering with a present illness can worsen it and delay the effects of present or future treatment.
Complications due to self-medication can cause damage to your body system. Drug misuse and abuse can lead to overdose, poisoning and unpleasant drug reactions, which can damage organs such as the liver, heart, kidneys, brain and skin. Damage to the body may cause disability.
Pregnant women who practise inappropriate self-medication also endanger the health of their unborn children.
Self-medication can cause or worsen mental health illnesses such as substance use disorder, depression and anxiety.
Self-medication can also be indirectly responsible for a person's mental health illness due to suffering from physical health consequences of harmful self-medication.
Death due to self-medication can result from complications such as negative drug reactions, taking the wrong drugs, drug overdose, organ damage, mental health illness and prolonged suffering.
Self-medication can also lead to spontaneous abortion.
With AMR on the rise, the chances of an increase in the rate at which infections and diseases spread in the African population are high.
Since these drug-resistant illnesses become harder to cure, they are more likely to spread widely before an effective alternative treatment plan is established.
Drug misuse and abuse due to self-medication causes AMR, which makes infections and diseases difficult to treat and more likely to spread.
Not only does this make people spend more on treating prolonged illnesses, but the government also spends more on
Additional healthcare expenses caused by the adverse effects of self-medication can limit the resources available for other nation building efforts.
Consequences and health complications caused by self-medication, such as drug resistance, organ damage, drug-induced illnesses and mental health illnesses, can lead to death.
The widespread of drug-resistant illnesses can result in death in large numbers when effective alternative treatment isn't available.
A high rate of chronic disease, prolonged illness and death in a population negatively affect the availability of human resources and and financial capital.
Whether out of their own action or inaction, when people perceive increases in death and disability in the community with unattended spread of diseases, they become cynical and lose confidence in the ability of their health system to meet their needs. This impacts negatively on governance at multiple levels.
Since self-medication is common in low income people and communities, failure to tackle it promotes the practice among them. This reinforces the existing inequity in the health system that favours the rich and endangers the poor.
An example of this inequity is that children from poor homes who are medicated inappropriately are more likely to die of malaria than those from rich homes who receive appropriate care.
Self-medication is a risky practice that can lead to incorrect diagnosis, drug misuse and abuse, delayed diagnosis and proper care, harmful drug reactions and drug resistance.
Complications from self-medication can also lead to prolonged suffering from an illness, organ damage, mental health disorders and even death.
Inappropriate self-medication also has several negative public health impact in Africa, including a high mortality rate, a higher risk of disease transmission, and higher healthcare expenditure.
Public and patient education on drug use, improvement and proper enforcement of drug laws and access to affordable quality public healthcare are some of the strategies to reduce the prevalence of harmful self-medication.
1. Oyediran, O. O., Ayandiran, E. O., Olatubi, M. I., & Olabode, O. (2019). Awareness of risks associated with Self-medication among Patients attending General Out-patient Department of a Tertiary Hospital in South Western Nigeria. International Journal of Africa Nursing Sciences, 10, 110–115.
2. Ruiz M. E. (2010). Risks of self-medication practices. Current drug safety, 5(4), 315–323.
3. Bennadi D. (2013). Self-medication: A current challenge. Journal of basic and clinical pharmacy, 5(1), 19–23.
4. World Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance. (2021), November 17 2021. Retrieved April 12, 2023
5. World Health Organization. Health inequities and their causes. February 22, 2018. Accessed May 2, 2023.
Self-medication in Africa: 4 commonly misused drug categories
Self-medication in Africa: What you need to know
Published: May 9, 2023
© 2023. Datelinehealth Africa Inc. All rights reserved.
Permission is given to copy, use and share content without alteration or modification and subject to attribution as to source.
DATELINEHEALTH AFRICA INC., is a digital publisher for informational and educational purposes and does not offer personal medical care and advice. If you have a medical problem needing routine or emergency attention, call your doctor or local emergency services immediately, or visit the nearest emergency room or the nearest hospital. You should consult your professional healthcare provider before starting any nutrition, diet, exercise, fitness, medical or wellness program mentioned or referenced in the DatelinehealthAfrica website. Click here for more disclaimer notice.