By: Adebowale Bello, Freelance Health Writer. With medical review and editorial support by the Datelinehealth Africa Team
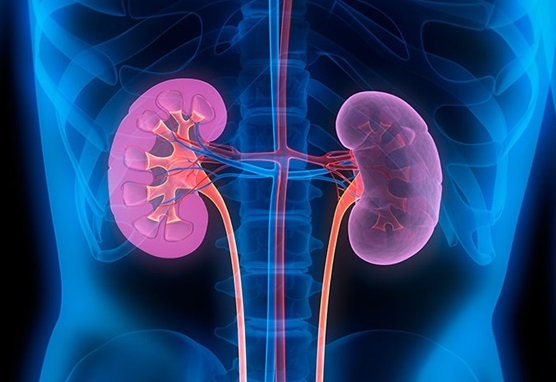
Illustration showing the kidneys lying below the rib cage in the back area of the upper abdomen.
Your kidneys are amazing organs, though you may not consciously attach much significance to them. However, this pair of bean-shaped organs are crucial to your overall well-being and this is because they serve as a natural filtration system that eliminates toxic waste from the bloodstream through the urine.
Apart from the removal of waste, the kidneys regulate the blood pressure and maintain the body's internal fluid and chemical balance, known as homeostasis.
As World Kidney Day was marked recently, this article aims to raise awareness and educate Africans, especially about the kidney; what it does, how it may be damaged, and how you can take care of your kidneys to live a healthy life.
The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs located just below the rib cage and to the left and right of your spine. They are linked to the bladder through two thin tubes of muscle called ureters, one on each side of your bladder. The urine formed in the kidneys passes through the ureters and is stored in the bladder. Your kidneys, ureters, and bladder are part of your urinary tract. (see fig 1)
Fig. 1: Illustration of the human urinary tract. Photo credit, NIDDK. Click image to enlarge.
On the top of each kidney is the adrenal gland, which is responsible for the production of several hormones, such as the stress hormone cortisol, aldosterone and adrenaline. The adrenal glands have no direct role in the functions of the kidneys.
The kidney can be segmented into an outer layer known as the renal cortex and an inner layer known as the renal medulla. (see fig. 2)
Fig. 2: An illustration of a cross section of the gross kidney showing an outer cortex and inner medulla. Click image to enlarge.
The renal cortex consists largely of renal corpuscles, which are specialised structures involved in the blood filtration process. The renal corpuscles are made up of the glomeruli which form from a meshwork of blood vessels and the two layered Bowman's capsule. It opens into a tubular system. The initial stage of filtration of blood for waste and excess fluid occurs in the cortex of the kidney as the blood passes through the glomeruli in the renal corpuscles (see Fig. 3)
.jpg)
Fig.3: Illustration of the composition of the nephron in the cortex and medulla of the kidney
The renal medulla contains the renal pyramids, which are cone-shaped structures that appear striped. However, it is the nephron that partitions each renal pyramid, giving it the striped appearance. The renal medulla regulates the amount of water to be reabsorbed from urine, thereby concentrating the urine before it leaves the kidneys. (see figure 3)
The kidneys play a crucial role in filtering waste products and excess substances from the blood to maintain proper balance within the body. Here's how the process works:
Blood pressure forces fluid, waste products, electrolytes and water out of the blood and into the surrounding Bowman's capsule, a structure that encases the glomerulus.
Although the main function of the kidney is to remove waste products, such as uric acid, creatinine and excess fluid and electrolytes (salts), it also performs several additional functions that include:
Just like every other organ, different diseases affect the kidney and they could either be short-term (acute) or long-term (chronic).
Here are four of the most common kidney diseases.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a kidney disease that begins slowly and progresses over a long time. The kidney is therefore unable to properly filter the body's waste and this waste accumulates gradually, which can lead to several other health problems. In 2017, an estimated 850 million people lived with CKD and with the increase in its risk factors, these numbers are steadily on the rise.
To differentiate CKD from other kidney diseases, a test known as the Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) is carried out to check your kidney function and if the test results are low for 90 days, it confirms CKD.
There are several medical conditions which may increase your risk of developing chronic kidney disease and some of these risk factors include:
The progressive nature of chronic kidney disease means you may likely not notice any symptoms out of the ordinary but as the disease progresses, you might begin to experience symptoms like
Minerals in the body can form solid masses, which may be tiny or huge. These masses are known as kidney stones or renal calculi (see fig. 4) and if you do have them, you may pass out the smaller stones while urinating. However, the bigger kidney stones may block the urinary tract, also known as the ureter.
The presence of the larger urinary stones in the ureter makes it extremely difficult to pass out urine, thereby causing severe pain. According to the National Kidney Foundation, 1 out of 10 people will have a kidney stone in their lifetime, thereby showing how common this condition is.
Some likely causes of kidney stones include:
Kidney stones are majorly characterised by abdominal pain, which may either be dull or sharp and this pain can occur in one side of your belly or feel like it's all over.
Other symptoms of kidney stones include:
There are 4 types of kidney stones and this is because of different compounds that form them (see fig. 4).
Figure 4: Showing varieties of kidney stones. Courtesy: Kumar A.
Click image to enlarge.
The different types of kidney stones include;
1. Uric acid stones
This makes up at least 10% of all kidney stones. The stones form when the uric acid levels in the urine are high. These high levels are due to increased consumption of foods that contain purine, such as fish, beef and poultry.
2. Struvite stones
A struvite stone is formed when bacteria leads to an upper urinary tract infection. These stones grow fast and can become large enough to block the urinary tract. In most cases, the stone is broken down and removed surgically.
3. Calcium oxalate stones
This is the most common type of kidney stones and it occurs when there is too much of the naturally occurring compound known as oxalate. This substance can be found in fruits, grains and nuts, while your body also produces it as a waste product. However, when you don't drink enough water, oxalate binds with calcium in bits until it forms a big stony mass.
4. Cystine stones
Cystine is an amino acid that performs different roles in the body, from aiding digestion to boosting the immune system. However, cystine stones can be formed when excess cystine is present in the urine and this is caused by cystinuria, which is a rare condition. Cystine stones might reoccur because cystinuria is a lifelong condition, however, if managed properly, formation of stones will cease.
Though rare, cystine stones are the most common inheritable cause of kidney stones worldwide and it affects more males than females.
Glomerulonephritis is the inflammation of the glomeruli, which are the tiny filters in the kidneys responsible for removing waste products and excess fluids from the blood to form urine. This inflammation can impair the kidney's ability to filter blood properly, leading to various symptoms and complications.
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a sudden and rapid decline in kidney function, leading to the accumulation of waste products and fluids in the body. It can occur rapidly over hours or days and there is a sudden decrease in urine output and/or an increase in serum creatinine levels.
There are three main categories of tests which can be carried out to determine the health of your kidneys and these tests are discussed below.
Urine tests are diagnostic tests that analyse the urine to provide information about various aspects of a person's health. Some common urine tests include:
Blood tests are diagnostic procedures that involve analysing blood samples to assess various aspects of health. These tests play a crucial role in diagnosing medical conditions, monitoring treatments and evaluating kidney function.
Some blood tests commonly used to assess kidney function include:
These are medical procedures that depict the inside of the body. These tests are carried out to help your doctor make an accurate diagnosis of the kidneys.
Some of the tests are;
Treatment for kidney diseases vary depending on the specific condition and its severity. Here's an overview of common treatments:
Fig. 5: Examples of kidney friendly African foods. Left: Yam, Right: spinach. Click image to enlarge.
Dialysis is a medical procedure that artificially removes waste and excess fluids from the blood and there are two types of dialysis; hemodialysis, which involves using a machine to filter blood outside the body, and peritoneal dialysis, which uses the lining of the abdomen to filter blood internally.
Transplant recipients usually require lifelong immunosuppressive medications to prevent rejection of the donor organ.
Taking care of your kidneys is important if you want to remain healthy and free from kidney disease. Here are some important tips for you:
Drinking an adequate amount of water helps to keep the kidneys functioning properly by flushing out waste products from the body. This is not always easy as the urge to drink flavour filled soft drinks is always high. However, you can get a water bottle and set occasional alarms on your mobile devices to remind you to drink water.
If your circumstances permit, you can make it a goal to drink between 2.5 to 3.5 litres of water daily.
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables can support kidney health. Consumption of processed foods which contain saturated fats, sugars and salts increase your risk of high blood pressure, diabetes and obesity, which are major risk factors for kidney disease.
High blood pressure can damage the kidneys over time so it's important to monitor your blood pressure regularly and take steps to keep it within a healthy range. You can do this by exercising regularly, reducing salt intake and taking prescribed medications.
If you live with diabetes, follow the management plan recommended by your doctor and constantly monitor your blood sugar levels.
Whether you've been smoking for decades or just started, one thing is sure;
Smoking is bad for your health.
Smoking can impair kidney function and increases your risk of kidney disease, hence quitting smoking is vital in prolonging your healthy kidneys.
If you're finding it difficult to quit smoking, seek support from doctors , counsellors, or smoking cessation programs designed to help you quit smoking.
Excessive alcohol consumption is a risk factor for many medical conditions including kidney failure. If you must drink alcohol, do so in moderation.
Engaging in regular physical activity can help you to maintain a healthy weight, lower blood pressure and improve cardiovascular health, all of which support kidney health. Setting aside 30 minutes daily to perform exercises like jogging, yoga and swimming can help you meet up with the 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise recommended by health guidelines.
In summary, understanding the kidney and how it works is crucial as it enables you to make informed health decisions. These decisions would let you prioritise your health and wellness as well as enlighten those around you.
1. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. [Internet, June 2018] . Your Kidneys & How They Work. Accessed March 13,2024.
2. Cleveland Clinic. [Internet, May 2022]. Adrenal Gland. Available from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/23005-adrenal-gland. Accessed March 13,2024.
3. National Kidney Foundation. [Internet, n.d]. How Your Kidneys Work. Available from https://www.kidney.org/kidneydisease/howkidneyswrk. Accessed March 13, 2024.
4. Kovesdy CP. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease: an update 2022. Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 2022 Apr;12(1):7-11. doi: 10.1016/j.kisu.2021.11.003. Epub 2022 Mar 18. PMID: 35529086; PMCID: PMC9073222. Accessed March 13, 2024.
5. Mayo Clinic. [Internet, September 2023]. Chronic kidney disease. Available from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/chronic-kidney-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20354521. Accessed March 18, 2024.
6. National Kidney Foundation. [Internet, n.d]. Uric acid stones. Available from https://www.kidney.org/atoz/content/uric-acid-stone. Accessed March 18, 2024.
7. National Kidney Foundation. [Internet, n.d]. Struvite stones. Available from https://www.kidney.org/atoz/content/struvite-stone. Accessed March 18, 2024.
8. National Kidney Foundation. [Internet, n.d]. Calcium oxalate stones. Available from https://www.kidney.org/atoz/content/calcium-oxalate-stone. Accessed March 18, 2024.
9. National Kidney Foundation. [Internet, n.d]. Cystine stones. Available from https://www.kidney.org/atoz/content/What-are-cystine-stones. Accessed March 18, 2024.
10. Stephen W. Leslie; Hussain Sajjad; Lama Nazzal. [Internet, May, 2023]. Cystinuria. Available from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470527/#:~:text=Cystine%20stones%20are%20due%20to,to%20the%20development%20of%20stones. Accessed March 18, 2024.
11. Bello, A. K., Okpechi, I. G., Osman, M. A., Cho, Y., Htay, H., Jha, V., Wainstein, M., & Johnson, D. W. (2022). Epidemiology of haemodialysis outcomes. Nature Reviews Nephrology, 18(6), 378-395. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-022-00542-7. Accessed March 21, 2024
Published: March 21, 2024
© 2024. Datelinehealth Africa Inc. All rights reserved.
Permission is given to copy, use and share content for non-commercial purposes without alteration or modification and subject to attribution as to source.
DATELINEHEALTH AFRICA INC., is a digital publisher for informational and educational purposes and does not offer personal medical care and advice. If you have a medical problem needing routine or emergency attention, call your doctor or local emergency services immediately, or visit the nearest emergency room or the nearest hospital. You should consult your professional healthcare provider before starting any nutrition, diet, exercise, fitness, medical or wellness program mentioned or referenced in the DatelinehealthAfrica website. Click here for more disclaimer notice.